How to Stay Positive After a Hearing Loss Diagnosis
Learning that you have hearing loss can bring many emotions, from
By: admin | July 24, 2024
Hormones, our body’s chemical messengers, play a huge role in everything from our metabolism to our mood. But, did you know they can also affect your hearing? This often overlooked aspect of hearing health is quite intriguing. Let’s take a closer look at the complex workings of your auditory system and the important role hormones play in shaping your auditory experiences.
Hormones aren’t just mood and metabolism regulators. They also greatly influence our hearing abilities. Hormones like estrogen, progesterone and even insulin can affect the health of your ears in various ways. They manage blood flow to the ears, control fluid levels in your inner ear and ensure your auditory system is working at its best. However, hormonal imbalances, which can occur due to stress, aging or certain medical conditions, can upset this delicate balance and potentially lead to hearing problems.
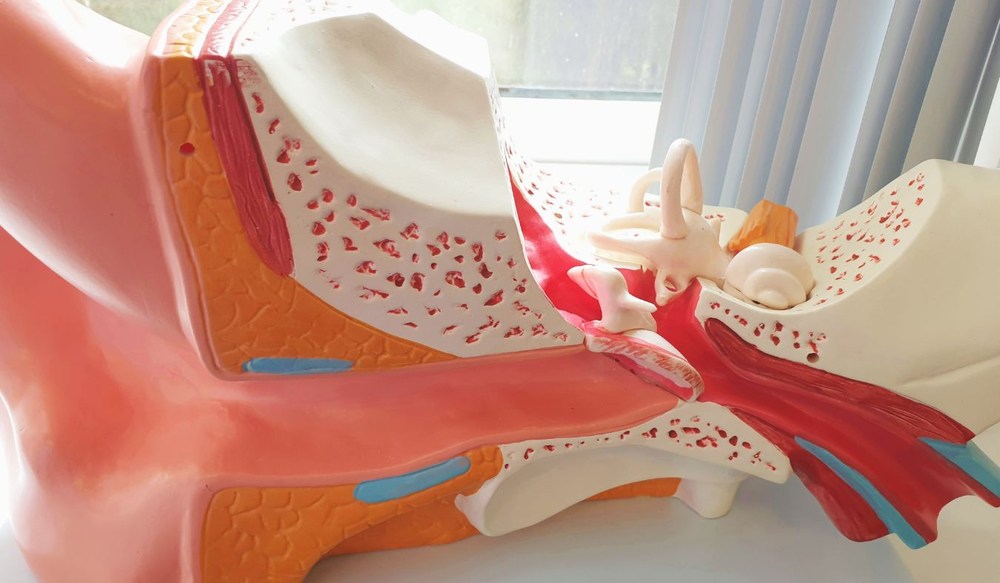
Our auditory system is responsible for the complex process of hearing. It operates in three stages: capturing sound waves with the outer ear, interpreting these waves in the middle ear and finally translating these vibrations into electrical signals in the inner ear that our brain interprets as sound. This complex operation happens seamlessly and instantaneously, allowing us to connect with our environment.
This system is efficient, capable of picking up a wide range of frequencies, and helps us identify where sounds are coming from. However, it’s not invincible. The delicate structures within our ears are susceptible to damage from loud noises. As we age, the efficiency of our auditory system can decline, leading to hearing loss. Additionally, certain diseases can negatively affect parts of our auditory system, leading to temporary or permanent hearing loss.
The connection between hormones and hearing is a fascinating one. This link isn’t as well-known as some other aspects of hearing health, but it’s just as important.
So next time you think about your hearing health, keep in mind that it’s not just about volume control or avoiding loud noises – it’s also about keeping an eye on those tiny chemical messengers buzzing around inside you!
Estrogen, predominantly found in women, has a noteworthy influence on hearing abilities. This hormone plays a significant role in maintaining the health of your auditory system. Research suggests that fluctuations in estrogen levels can lead to changes in hearing sensitivity.
Estrogen helps regulate blood flow throughout the body, including the ears. Changes in estrogen levels can disrupt this regulation, potentially leading to issues with hearing. Menopause can affect your hearing due to a drop in estrogen levels during this time. Some women may experience changes in their hearing sensitivity. While it’s not always possible to prevent hormonal-related hearing loss completely, maintaining overall good health and regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help manage potential risks.
If you’re noticing changes in your hearing or concerns about your hormone levels affecting it, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for advice and support.
Progesterone, often overshadowed by estrogen in discussions about women’s health, plays a unique and critical role in maintaining auditory well-being. This hormone, primarily known for its functions in the reproductive system, extends its influence to various other physiological processes, including hearing. Progesterone is known for its protective qualities, particularly when it comes to safeguarding the delicate structures within the ears. Studies suggest that it helps shield these auditory structures from damage, thereby supporting overall hearing health.
The inner ear contains tiny hair cells that are essential for converting sound waves into electrical signals, which the brain then interprets as sound. Progesterone contributes to the maintenance and repair of these hair cells, ensuring they function optimally. When progesterone levels are balanced, they can help prevent the deterioration of these cells, reducing the risk of hearing loss. This protective effect highlights the importance of progesterone in preserving hearing abilities and preventing auditory decline.
Imbalances in progesterone levels, however, can potentially lead to changes in hearing abilities. Fluctuations in this hormone, which can occur naturally due to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, menopause or certain medical conditions, may impact the auditory system. For instance, women may experience temporary changes in hearing sensitivity or an increased risk of hearing issues during periods of hormonal imbalance. These changes underscore the need for monitoring progesterone levels and understanding their impact on hearing health.
It’s important for women to be aware of how hormonal fluctuations can affect their hearing and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and hormonal assessments can help identify imbalances early on, allowing for timely intervention and management. By maintaining balanced progesterone levels through lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments or hormone therapy, women can support their auditory health and reduce the risk of hearing loss.
The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland located in your neck, produces hormones that play a crucial role in regulating your body’s metabolism. These thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are essential for the proper functioning of various bodily systems, including the cardiovascular, nervous and muscular systems. However, their influence extends beyond these primary functions, significantly impacting the health and functioning of your ears and overall auditory system.
Thyroid hormones ensure optimal blood flow to the ears, a critical factor for maintaining healthy auditory function. Adequate blood flow delivers essential nutrients and oxygen to the delicate structures within the ears, such as the cochlea, hair cells and auditory nerves. This nourishment is vital for the proper functioning and longevity of these components, enabling them to convert sound waves into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. Any disruption in blood flow can compromise the health of these structures, potentially leading to hearing issues.
In addition to regulating blood flow, thyroid hormones also play a role in the growth and maintenance of cells within the auditory system. These hormones help regulate cellular metabolism, ensuring that cells in the ears grow, function and repair themselves effectively. Proper cellular function is essential for maintaining the integrity of the auditory system and preventing damage that could lead to hearing loss.
Imbalances in thyroid hormones, due to conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), can have a profound impact on hearing abilities. Hypothyroidism, characterized by insufficient production of thyroid hormones, can lead to reduced blood flow and slowed cellular metabolism in the ears. This can result in symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears) and dizziness. Conversely, hyperthyroidism, characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones, can cause increased blood flow and metabolic activity, potentially leading to inner ear disturbances and hearing issues.
The connection between thyroid health and hearing underscores the intricate interdependence of our body’s systems. Maintaining overall health, including thyroid function, is essential for preserving good hearing. Regular check-ups and monitoring of thyroid hormone levels can help detect imbalances early on, allowing for timely intervention and management. Treatments for thyroid imbalances, such as hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism or medications to regulate hormone production in hyperthyroidism, can help restore proper thyroid function and mitigate their impact on hearing health.
Testosterone, a vital hormone in male health, significantly influences various bodily functions, including the auditory system. This hormone helps regulate and maintain numerous physiological processes, contributing to overall well-being. Recent research indicates that testosterone levels can directly impact hearing abilities. Men with lower testosterone levels have been found to experience higher rates of hearing loss, suggesting a crucial link between hormone balance and auditory health.
The auditory system relies on a delicate balance of cellular and biochemical processes to function correctly. Testosterone is known to support the maintenance and repair of these auditory structures. When testosterone levels are low, the cells within the inner ear may not function optimally, leading to a decline in hearing capabilities. This can result in difficulties in distinguishing sounds, understanding speech and maintaining overall auditory clarity. Ensuring balanced testosterone levels is essential for preserving good hearing health.
Maintaining optimal testosterone levels involves various lifestyle and medical approaches. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep and stress management can naturally support healthy testosterone levels. For men experiencing significant hormonal imbalances, medical interventions such as hormone replacement therapy may be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. By addressing testosterone levels, men can not only enhance their overall health but also protect their hearing abilities, ensuring better communication and quality of life.
Menopause brings numerous changes to the body, including fluctuations in hormone levels that can impact your hearing. The drop in estrogen and progesterone levels during menopause can lead to alterations in hearing sensitivity, making it more difficult to hear certain frequencies. These hormonal shifts can also increase the risk of hearing loss, potentially linked to osteoporosis and other age-related conditions. Additionally, this stage of life can bring about the onset of tinnitus, a persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears that can significantly affect one’s quality of life.
Pregnancy is a period of significant hormonal changes, with increases in estrogen and progesterone. These hormonal shifts can affect your hearing in various ways. Increased fluid retention during pregnancy can lead to changes in blood flow to the ears, potentially impacting auditory function. Hormonal fluctuations can also alter the pressure in the middle ear, affecting hearing sensitivity. Additionally, some women may experience tinnitus, a persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears, which can be particularly bothersome during pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the delicate equilibrium that maintains your auditory health. These imbalances can occur for various reasons and can lead to changes in hearing sensitivity, trigger tinnitus or contribute to hearing loss in some cases. It’s important to note that everyone’s experience with hormonal imbalances and their effects on hearing will be different.
Hormone-induced hearing loss may not be immediately noticeable. It often starts with subtle changes that might be easy to overlook. However, being aware of these potential signs can help you seek timely help from a healthcare provider. If you’re experiencing changes in hearing sensitivity, tinnitus or difficulty understanding speech, it’s best to consult with an audiologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Maintaining balanced hormones for healthy ears is achievable with a few straightforward strategies. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep and stress reduction all contribute to hormone balance. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor any potential hormonal imbalances that could affect your auditory system.
Understanding the impact of hormones on your hearing health can be a complex task, but you don’t have to do it alone. If you’ve noticed changes in your hearing or if you have concerns about how hormonal shifts could be affecting your auditory abilities, reach out to the team at Ashbrook Audiology. Conveniently located in Virginia, you can contact one of our offices at Danville: (434) 792-2182 or Martinsville: (276) 666-0401. Let’s work together towards maintaining your optimal hearing health – because every sound matters!

Learning that you have hearing loss can bring many emotions, from
By: admin | November 18, 2025

When someone you care about begins to experience hearing loss, it is not
By: admin | September 24, 2025
Travel opens up new experiences and adventures, but it can also bring
By: admin | April 24, 2025
